
What is Acne?
Acne is a common chronic skin condition that occurs when hair follicles (pilosebaceous unit) become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to the formation of microcomedones (small “clogged pores” with no opening), blackheads, whiteheads, and other types of lesions.
It can occur on any part of the body but is most commonly seen on the face, chest, and back. The medical term for acne is “acne vulgaris”. Acne is more than just a physical illness because it can cause substantial psychological and social issues for the patient especially if acne blemishes develop on the skin.
Therefore, intervention and early acne treatment are important to not only treat acne but also to prevent scarring as much as possible.
What Are The Causes Of Acne?
Genetics
Acne breakouts tends to run in families, so if your parents or siblings have had acne, you may be more likely to develop it.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal changes during puberty, menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and menopause can all contribute to the development of acne.

Increased Oil (Sebum) & Skin Cells (Hyperkeratinisation) Production
Bacteria
Cutibacterium acnes (C. acnes) is a type of bacteria that is normally found on the skin but can cause acne when it colonises the follicle. [note: (Propionibacterium acnes was renamed to Cutibacterium acnes in 2016]
Inflammatory Reaction & Oily Skin
Fungus/Yeast (Pitysporum Folliculitis)
Can be associated with seborrheic dermatitis (on scalp – “dandruff”)
Environmental Factors
Air pollution, temperature, humidity, grease contact (kitchen)
Lifestyle Factors
Diet (dairy, whey protein, sugar), stress (can affect hormones), tight-fitting clothing, hygiene, hair washing/drying habits, picking at lesions, makeup, skin care products, and certain medications can all contribute to the development of acne.

Types of Acne Lesions
Microcomedones
Commonly not visible to the naked eye, they are the precursor to other acne lesions. There is commonly microscopic excess oil and dead skin cells blocking the follicle.
Comedones
Known as clogged pores. Small, raised bumps on the skin, that can be ‘open’ (blackheads) or ‘closed’ (whiteheads) depending on whether the follicle opening is covered or not by the skin.
Papules
Small, red bumps that are raised above the surface of the skin.
Cysts
Similar to nodules in size and depth but are filled with pus and can be softer to the touch. Cysts are often larger than other acne lesions and can be quite painful. (See below above)
Nodules
Larger, more severe lesions that develop deeper within the skin. They are firm, painful, and can be deeply embedded. Nodules are often accompanied by inflammation and may take longer to heal compared to other types of acne lesions. (See above image)
Pustules
Similar to papules, but with a white or yellow centre filled with pus. Commonly with inflammation (redness, pain, swelling) around the lesion. (See image above)
Assessing Acne Problems
Primary assessment of patients with acne starts with a proper history taking. Due to the multifactorial nature of acne, family history, environmental factors, diet, hygiene, makeup/skincare products, stress, physical activity, and medication history need to be evaluated. Close examination of the skin for comedones which can develop into more severe types of acne lesions is required in addition to the assessment of other larger acne lesion types and locations on the face/body.
Examination of the scalp is also needed to rule out any fungus/yeast component that may contribute to acne.
Effective treatments for acne in Singapore as well as acne scar treatment depend on the severity and types of acne, as well as the individual patient’s skin type and medical history. As acne can also affect children and teenagers, the age-specific safety of certain treatments must also be taken into consideration.
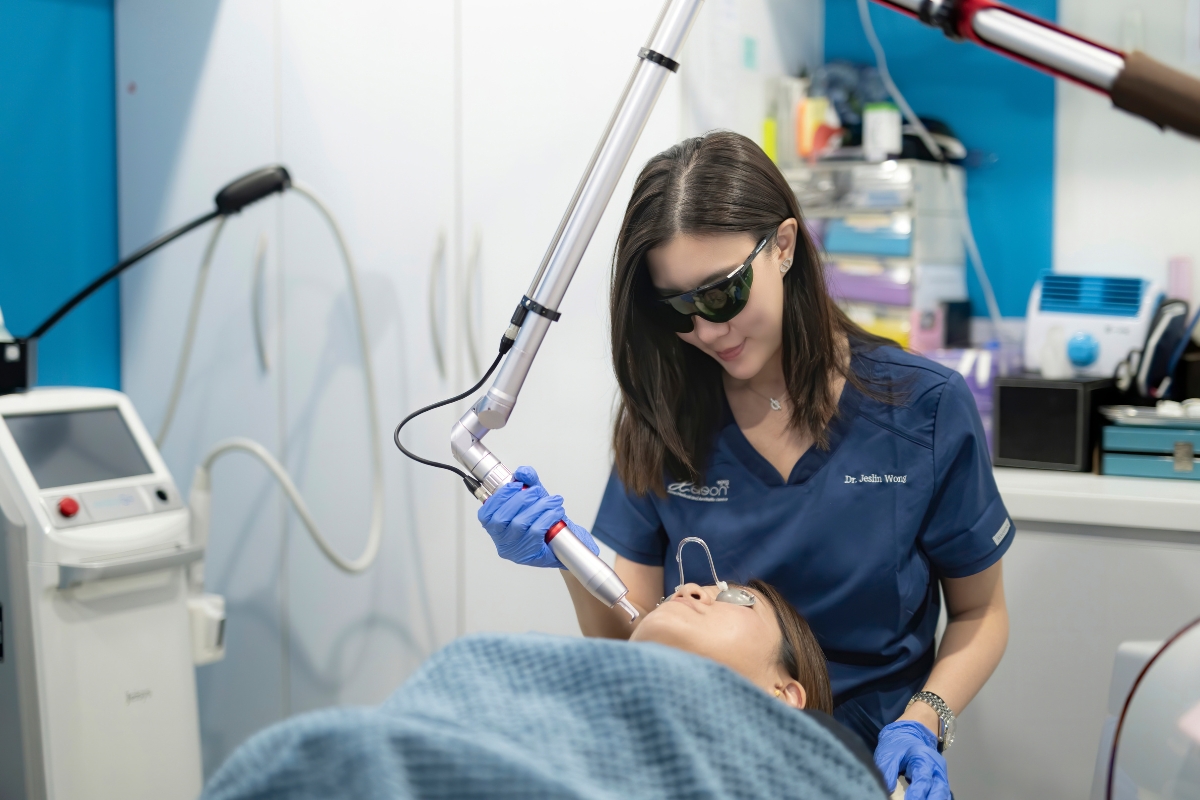
Types of Acne Treatments in Singapore
Acne is a very complex, chronic condition which is challenging to treat and can have long-term effects not only on the skin but also mentally and socially. Cooperation between the patient and the treatment team is important in achieving treatment goals. After these goals are met, maintenance to prevent the recurrence of acne is vital. Once acne maintenance is achieved, treatments on how to get rid of acne scars can be taken into consideration.
Help to prevent and reduce non-inflammatory lesions (comedones). Important in the maintenance stage after treatment goals have been reached. Includes appropriate cleanser, AHA, BHA, benzol peroxide, azelaic acid, adapalene, and retinoids (tretinoin). Topical antibiotics are used to treat mild to moderate inflammatory acne. However, improper use may lead to resistance so they should be used in combination with other regimens and according to instructions by your dermatologist for acne. Topical antibiotics include clindamycin and erythromycin.

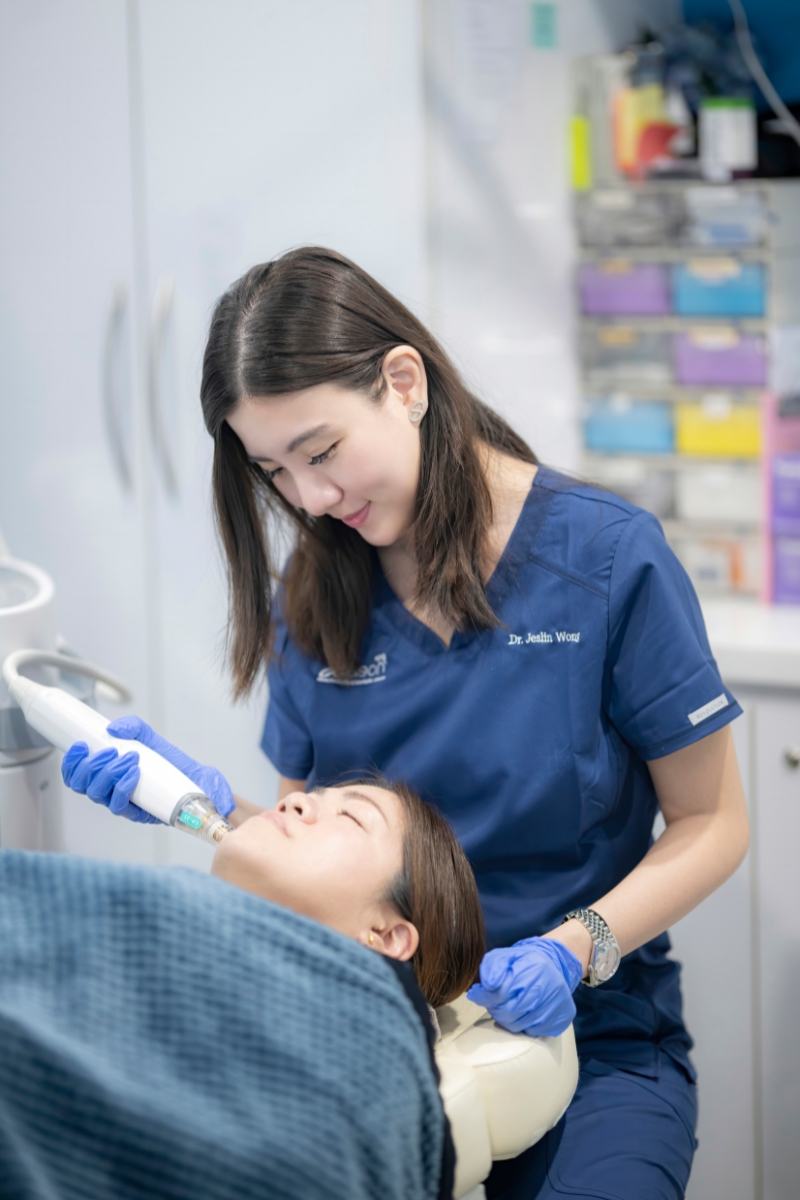
Find the Right Doctor for Acne Treatment in Singapore
Selecting the right acne doctor is essential for effective treatment and achieving clear, healthy skin. With Dr Jeslin Wong’s years of experience as a medical aesthetic doctor, you can feel assured that our team will come up with the right treatment plan to treat and reduce the appearance of acne.
By customising treatment plans tailored on individual needs, skin types and using effective technologies, our acne doctor improve your skin condition, giving you more confidence.
Ready to address your acne problems? Book an appointment with us today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Pimples and acne are often used interchangeably. However, both of them refer to different skin conditions. Acne is a disease that affects the skin’s hair follicles and sebum-producing glands, whereas pimples are a symptom of acne that appears on the skin when the glands overproduce sebum, causing the pore or follicle to get clogged. Once the pores are clogged, bacteria can cause inflammation that results in the production of a pimple. You may have pimples but not necessarily acne, while on the other hand, if you have acne, it will manifest itself in the form of pimples and other nodules.

Disclaimer
The information provided on this website is for educational purposes only and is, in no way, intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. We make no representation or warranty of any kind regarding the accuracy, availability, adequacy, or validity of the information or procedures outlined on the website. Always consult professional medical and aesthetic advice for your skincare and medical concerns.
References:
- Elika Hoss, MD, Assistant Professor of Dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ, "Acne - self-care", National Library of Medicine, 2024, https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000750.htm
- John Kraft, MD and Anatoli Freiman, MD, "Management of acne", National Library of Medicine, National Center for Biotechnology Information, 2011, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3080563/
- "Acne: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Steps to Take", National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/acne/diagnosis-treatment-and-steps-to-take
Contact Us
Talk to our friendly AEON team by filling out the form. We will get back to you within 2-3 working days. For a faster response, contact our hotline below.
Call us anytime
Address
9 Scotts Rd, #06-01/02/03 Scotts Medical Centre, Pacific Plaza Singapore 228210
